G-7 Weighs De Minimis Tariffs On Chinese Imports

Table of Contents
Understanding De Minimis Tariffs and Their Current Impact
De minimis tariffs refer to the value threshold below which imported goods are exempt from import duties or customs duties. This "de minimis value" is set by each country and acts as an import duty threshold, allowing for low-value shipments to enter without incurring tariffs. The current de minimis levels for Chinese imports vary across G7 countries, significantly impacting import volumes and the competitiveness of businesses, particularly small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs).
-
Impact on SMBs: Lower de minimis values can create a disproportionate burden on SMBs importing smaller, less expensive goods from China. The added tariff costs can erode profit margins and hinder their ability to compete with larger importers.
-
Government Revenue Implications: Current de minimis thresholds directly influence government revenue collected from import tariffs. Higher thresholds generally lead to less revenue collected from smaller shipments.
-
Product Category Impact: Certain product categories are more significantly affected than others. For example, smaller consumer electronics, clothing items, and certain types of manufactured goods are disproportionately influenced by de minimis tariff adjustments. These often represent a significant portion of imports from China.
G7's Deliberations on Adjusting De Minimis Tariffs
The G7's ongoing discussions surrounding de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports reflect broader concerns about trade imbalances, unfair trade practices, and the need to protect domestic industries. These trade negotiations involve complex considerations, with potential motivations ranging from supporting domestic manufacturing to addressing perceived economic exploitation.
-
Key Players: The discussions involve key government agencies and officials from each G7 nation (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States), reflecting the high level of international coordination required.
-
Potential Scenarios: The G7 could decide to increase de minimis thresholds, decreasing the number of imports subject to tariffs; decrease thresholds, increasing tariff revenue and potentially protecting domestic industries; or maintain the status quo.
-
Political Sensitivities: Adjusting tariff policies related to China is fraught with political sensitivities, considering the complex bilateral relations and the broader geopolitical landscape. Any decision will undoubtedly have significant international implications.
Economic and Political Implications of the G7 Decision
Altering de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports will have wide-ranging economic and political consequences. The potential impacts extend beyond the G7 itself, influencing global supply chains and international relations.
-
Impact on Inflation: Increasing tariffs could contribute to inflationary pressures in G7 countries, as the cost of imported goods rises. Decreasing tariffs might offer some relief from inflation, but could also raise concerns about the competitiveness of domestic industries.
-
Global Supply Chain Shifts: Changes to de minimis tariffs could disrupt existing global supply chains, forcing businesses to re-evaluate sourcing strategies and potentially leading to increased costs and delays.
-
Potential Retaliatory Measures: China might respond to G7 actions with retaliatory measures, escalating trade tensions and potentially triggering trade wars or further economic sanctions.
Conclusion
The G7's decision on adjusting de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports presents a crucial juncture in global trade. While raising tariffs might offer short-term protection for domestic industries and increase government revenue, it could also lead to higher consumer prices and increased trade tensions. Lowering tariffs could boost economic growth by lowering import costs but might also raise concerns about job displacement in domestic industries. The potential consequences are complex and multifaceted, affecting global supply chains, economic growth, and international relations. Stay informed about the G7's final decision on de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports, as this will significantly impact global trade and businesses involved in importing goods from China. Follow our updates on the evolving situation surrounding de minimis tariffs and Chinese imports.

Featured Posts
-
 Le Borse Crollano A Causa Dei Dazi La Risposta Decisa Della Ue
May 24, 2025
Le Borse Crollano A Causa Dei Dazi La Risposta Decisa Della Ue
May 24, 2025 -
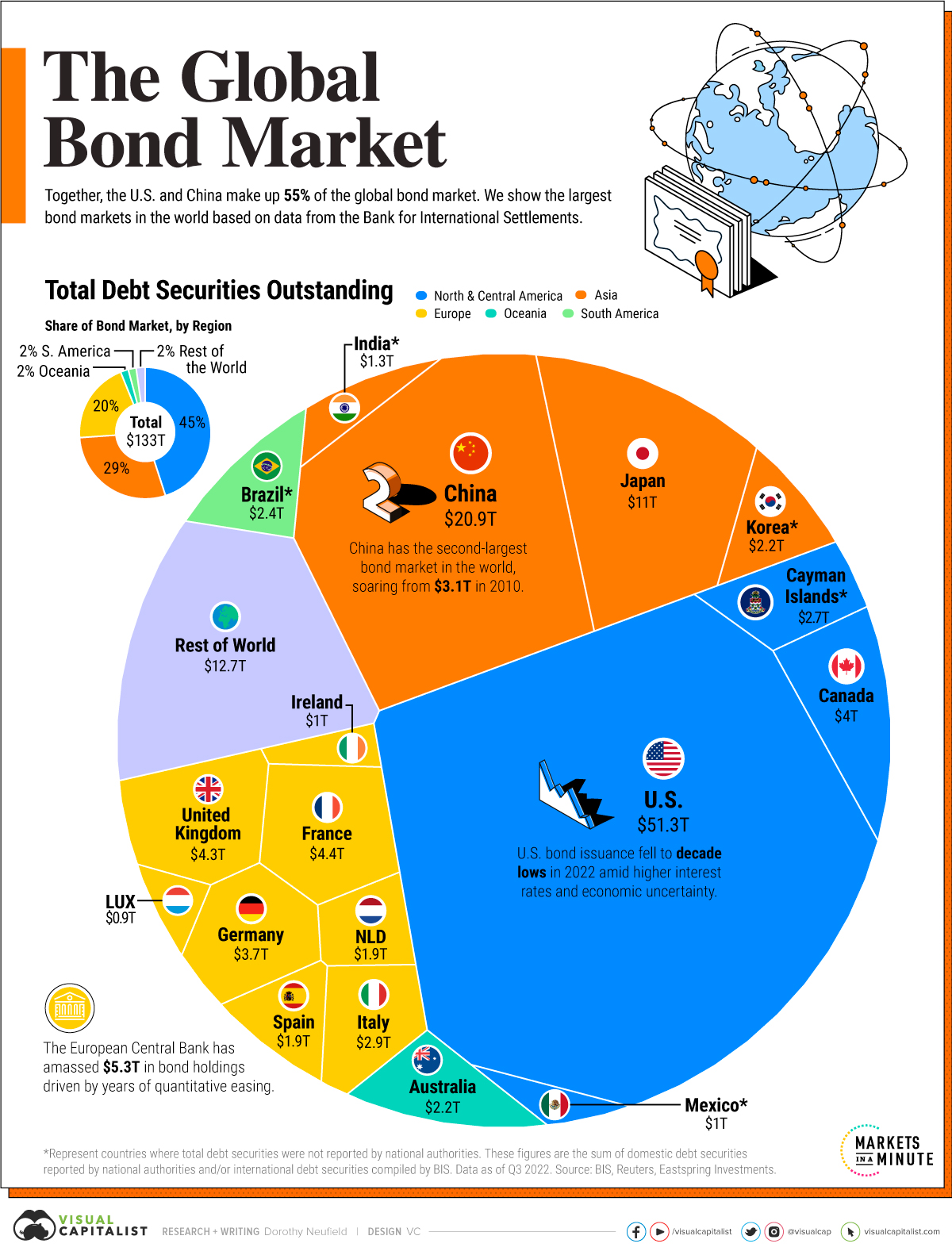 Is The Worlds Largest Bond Market In Trouble A Posthaste Perspective
May 24, 2025
Is The Worlds Largest Bond Market In Trouble A Posthaste Perspective
May 24, 2025 -
 Kakuyu Rol Olega Basilashvili Vy Znaete Luchshe Vsego Test
May 24, 2025
Kakuyu Rol Olega Basilashvili Vy Znaete Luchshe Vsego Test
May 24, 2025 -
 Your Ticket To Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 How To Buy
May 24, 2025
Your Ticket To Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 How To Buy
May 24, 2025 -
 Dax Rally Assessing The Risk Of A Wall Street Driven Market Correction
May 24, 2025
Dax Rally Assessing The Risk Of A Wall Street Driven Market Correction
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Horoscopo Semanal 11 17 Marzo 2025 Astrologia Para Todos Los Signos
May 24, 2025
Horoscopo Semanal 11 17 Marzo 2025 Astrologia Para Todos Los Signos
May 24, 2025 -
 Horoscope Highlights April 14 2025 Top 5 Zodiac Signs
May 24, 2025
Horoscope Highlights April 14 2025 Top 5 Zodiac Signs
May 24, 2025 -
 Horoscopo De La Semana Del 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025 Para Todos Los Signos
May 24, 2025
Horoscopo De La Semana Del 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025 Para Todos Los Signos
May 24, 2025 -
 Horoscopo Semanal Predicciones Del 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025
May 24, 2025
Horoscopo Semanal Predicciones Del 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025
May 24, 2025 -
 Dylan Dreyers Sons Surgery A Hospital Update
May 24, 2025
Dylan Dreyers Sons Surgery A Hospital Update
May 24, 2025
